A
Adjunctive Treatment / Procedures
adjunctive (in health care)- an additional substance, treatment, or procedure used for increasing the efficacy or safety of the primary substance, treatment, or procedure or for facilitating its performance.
[Return to Index]
Amenorrhea
Absence of menstruation, diagnosed when a woman does not have a period for three months or more.
[Return to Index]
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
AMH predicts a woman's remaining egg supply (ovarian reserve). AMH is produced by the granulosa cells in the ovarian follicles. AMH blood levels indicate the size of the pool of follicles remaining; therefore, as a woman ages, the size of the ovarian follicle pool decreases and the AMH level also decreases, becoming undetectable at the time of menopause.
[Return to Index]
Artificial reproductive technology (ART)
Technology that improves fertility and promotes pregnancy. This umbrella term covers infertility treatments such as IVF that process the egg and sperm.
[Return to Index]
Azoospermia
Azoospermia is the complete absence of sperm in a man's semen. It occurs in 5-10% of men who seek fertility treatment.
[Return to Index]
B
Beta hCG
A beta, or beta pregnancy test, is a blood test for the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). Levels of hCG increase steadily in the early stages of pregnancy, showing physicians that a healthy pregnancy is progressing.
[Return to Index]
Biochemical pregnancy
The medical term used to describe a very early miscarriage, which usually happens in the first couple of weeks after an embryo has been transferred to the womb.
[Return to Index]
Blastocyst
Five to six days after a zygote is created by the fusing of an egg and a sperm, it becomes a blastocyst, a multi-cell mass, and enters the uterus. This is also the stage at which the embryo is transferred into the uterus during an embryo transfer (day 5) or during a frozen embryo transfer (day 5 or 6).
[Return to Index]
BMI
Body-mass index - a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to men and women.
Underweight = < 18.5
Normal weight = 18.5 - 24.9
Overweight = 25 - 29.9
Obesity = > 30
Morbid obesity = > 40
[Return to Index]
C
Canadian Compliant
"Canadian Compliant" means that a donor's units meet the Health Canada Standards.
They require donor's units to have some additional testing done including Semen Culture, Gonorrhea, and Chlamydia by DNA on the day of donation.
[Return to Index]
Chemical pregnancy
Another term to describe a very early miscarriage, which occurs 1-2 weeks after an embryo has been transferred to the womb.
[Return to Index]
Clinical Pregnancy
A pregnancy that has been confirmed by two things: an ultrasound showing either a heartbeat or gestational sac (a fluid-filled structure in the uterus) and high levels of the pregnancy hormone hCG.
[Return to Index]
Clomiphene citrate/Clomid (product name)
A fertility drug used to trigger follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which can jump-start the ovulation process.
[Return to Index]
Controlled ovarian stimulation (COS)
The process of stimulating ovulation using fertility drugs (such as Clomiphene citrate or Letrozole, or Gonadotropins).
[Return to Index]
Corpus luteum
After an egg is released during ovulation, the structure it leaves behind is called the corpus luteum. It produces progesterone, which helps sustain a new pregnancy.
[Return to Index]
Cryopreservation
The process of freezing eggs or embryos from an ART cycle for potential future use.
[Return to Index]
Cycle Monitoring
This process occurs during the first half of the menstrual cycle to allow the doctor to follow the development of the follicles and eggs, and measure the hormone levels. It can be done in a natural cycle or while using fertility medication to stimulate the ovaries. It requires ultrasound and/or bloodwork each time the woman comes in.
[Return to Index]
D
Diminished ovarian reserve
This condition means that the ability of the ovaries to produce eggs is reduced.
[Return to Index]
Down-regulation
This is sometimes used as one of the first steps in IVF. The woman receives a drug that temporarily "switches off" her ovaries to better control ovulation and egg maturation during treatment. Fertility drugs are used to "switch on" your ovaries later. This process is also called "down regging," and the process is a "down-regulation cycle."
[Return to Index]
E
Endometrial biopsy or sampling
This is a test done in the doctor's office to study the lining of the uterus (endometrium). A sample of endometrial tissue is removed using a very fine catheter placed in the uterus. This test is usually done late in the menstrual cycle, after ovulation.
[Return to Index]
Endometriosis
A gynaecological condition in which the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside of the uterus. This tissue responds to hormones the way it normally would, and can grow on the ovaries causing cysts (called endometriomas), or on other structures within the pelvis. Because it also bleeds during menstruation, scar tissue may form within the pelvis, which can cause pain and distortion of structures. Inflammation usually occurs within the "implants" of endometriosis which affect various aspects of the reproductive process, leading to decreased fertility.
[Return to Index]
Estrogen (E2)
E2 refers to estradiol, or your level of estrogen. The estrogen level correlates directly with the number of follicles in your ovaries, helping physicians to estimate how many eggs you will have for retrieval during your cycle.
[Return to Index]
Ectopic pregnancy
A pregnancy in which the fertilized egg implants somewhere other than the uterus.
[Return to Index]
Egg retrieval, Egg collection, Ovum Pick-up (OPU)
An IVF treatment step in which eggs are removed from the ovaries using real-time ultrasound guidance, for use (immediate fertilization) or storage (egg freezing).
[Return to Index]
Embryo
An embryo is created when the sperm meets, penetrates, fuses with and fertilizes the egg, forming a single cell. The embryo then divides and develops into a multi-cell cluster. Further divisions create a morula and then a blastocyst.
[Return to Index]
Embryo transfer (ET)
The procedure of placing an embryo into a woman's uterus during in vitro fertilization (IVF).
[Return to Index]
F
Fallopian tubes
Two hollow tubes on either side of the uterus. The egg and sperm meet in one of the tubes to begin the fertilization process.
[Return to Index]
Fertilization
The penetration of the egg by the sperm and the combining of genetic material, which may result in pregnancy if the fertilized egg implants in the uterus.
[Return to Index]
Fetus
The embryo is called a fetus from the eighth week after conception to the moment of birth.
[Return to Index]
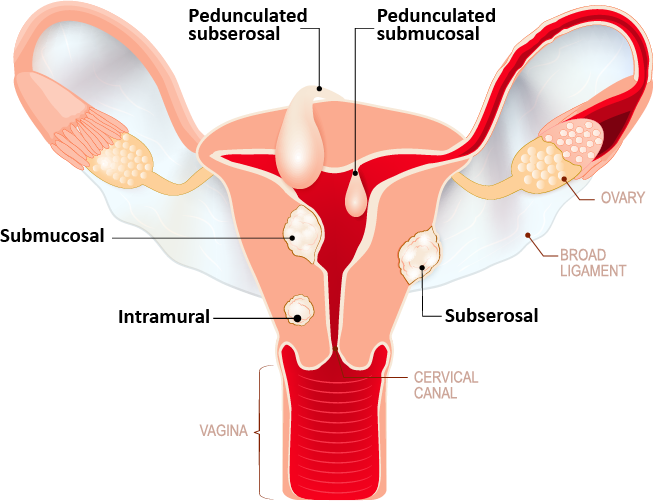
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer. They can cause decreased fertility, depending on their location and their size. They can also be associated with pain and heavy bleeding.
[Return to Index]
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
FSH is released by the brain to stimulate the ovarian follicles (structures within the ovaries, each containing a maturing egg) to grow and develop.
[Return to Index]
Frozen embryo transfer (FET)
A procedure in which the frozen embryos from a previous fresh IVF or donor egg cycle are thawed and then transferred back into a woman's uterus.
[Return to Index]
G
Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
This ART procedure extracts a woman's eggs, mixes them with sperm and immediately uses a catheter to place them into her fallopian tube to fertilize. It requires laparoscopic surgery and a general anesthetic. This is a rarely used alternative to traditional IVF.
[Return to Index]
Gestational carrier
A surrogate who carries a baby not genetically related to her; another couple's embryo is transferred to her uterus, she becomes pregnant and she gives birth to the baby.
[Return to Index]
Gestational sac
A fluid-filled structure that develops within the uterus early in pregnancy. The fetus grows inside the gestational sac.
[Return to Index]
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
A hormone that is involved in triggering ovulation.
[Return to Index]
H
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
HCG is a hormone produced during pregnancy. Levels of hCG increase steadily in the early stages of pregnancy, showing physicians that a healthy pregnancy is progressing. A beta pregnancy test specifically looks for and measures hCG.
[Return to Index]
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
An exam that determines the condition of the fallopian tubes and uterus. When an HSG is performed, dye is placed through the cervix into the uterus and fallopian tubes. An x-ray determines if the uterine cavity is normal and the tubes are open.
[Return to Index]
Hysteroscopy (HSC)
A procedure in which a thin, telescope-like instrument is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, allowing the doctor to see and photograph the area. This test is usually done with either a general or local anesthetic.
[Return to Index]
I
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
A fertility treatment used when sperm count is too low or sperm quality is too poor to effectively penetrate the egg on its own. An embryologist selects a single healthy sperm and injects it directly into the center of the egg. This has been a highly effective treatment for male factor infertility.
[Return to Index]
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
A method of assisted reproduction that involves combining an egg with sperm in a laboratory dish. If the egg is fertilized and the cells begin to divide, the resulting embryo is transferred into the woman's uterus, where it will hopefully implant in the uterine lining and further develop into a fetus.
[Return to Index]
Implantation
Within 6 to 7 days after an egg is fertilized, it implants in (attaches to) the lining of the uterus.
[Return to Index]
Infertility
Medically, if a woman is under age 35, she and her partner are experiencing infertility if they have not conceived after having 12 months of unprotected sex. If the woman is 35 or older, they are diagnosed with infertility after six months of trying.
[Return to Index]
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
A procedure involving placing sperm directly into a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization.
[Return to Index]
L
Laparoscopy
A procedure that involves insertion of a narrow, telescope-like instrument called a laparoscope through a small incision in the abdomen, allowing doctors to inspect various reproductive organs.
[Return to Index]
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
LH is produced by the gonadotropin cells in the pituitary gland. In women, the rise of LH (known as the "LH surge") triggers ovulation, or the release of an egg into a fallopian tube.
[Return to Index]
Luteal phase (LP)
The time between ovulation and menstruation (also called the two-week wait)
[Return to Index]
LH surge
A surge of luteinizing hormone helps the follicle rupture and the egg break through the surface of the ovary during ovulation. You can use an ovulation predictor kit, which detects the surge in LH in your urine, indicating that ovulation is likely within the next 12 to 24 hours. It can also be measured in your blood, indicating that ovulation is likely to occur within the next 24 - 36 hours.
[Return to Index]
M
Male factor infertility
When the cause of a couple's infertility is due to problems in the man or when it contributes to existing fertility problems in the woman.
[Return to Index]
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible.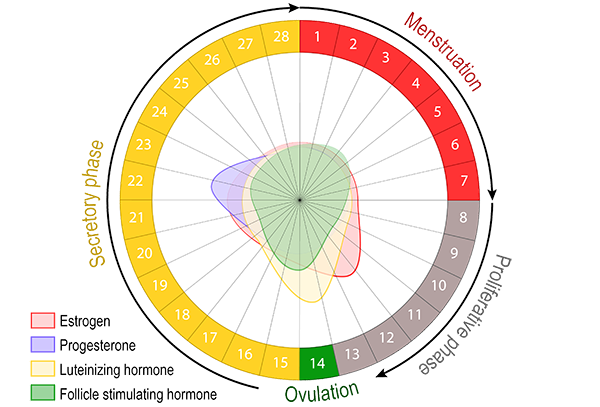
About once a month, females who have gone through puberty will experience menstrual bleeding. This happens because the lining of the uterus has prepared itself for a possible pregnancy by becoming thicker and richer in blood vessels, in response to hormonal changes. If pregnancy does not occur, this thickened lining is shed, demonstrated by bleeding. Bleeding usually lasts for 3-8 days. For most women, menstruation happens in a fairly regular, predictable pattern. The length of time from the first day of one period to the first day of the next period normally ranges from 21-35 days.
[Return to Index]
Microsurgical testicular sperm extraction (MicroTESE)
This minor surgical procedure removes a small sample of testicular tissue in order to retrieve sperm for use in an IVF cycle.
[Return to Index]
Miscarriage (also called spontaneous abortion)
A pregnancy ending in the spontaneous loss of the embryo or fetus before 20 weeks of gestation.
[Return to Index]
N
Natural cycle IVF
An IVF procedure that is done using your natural menstrual cycle, without fertility drugs to influence natural egg production.
[Return to Index]
O
Oligozoospermia (also oligospermia)
A condition in which a man has very few sperm, causing male factor infertility.
[Return to Index]
Ovulation
The release of eggs from the ovaries. In humans, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm.
[Return to Index]
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
A rare complication of ovarian stimulation to create egg growth. OHSS causes a woman to develop fluid in the abdomen and enlarged ovaries.
[Return to Index]
Ovarian stimulation
The use of medications to stimulate the ovaries to develop eggs.
[Return to Index]
P
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It usually occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from your vagina to your uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries. It often does not produce any or only mild signs or symptoms, and therefore may not be detected until much later. The common symptoms include lower abdominal pain, fever, nausea and vomiting, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge. It can cause obstruction of the fallopian tubes if it is untreated.
[Return to Index]
Progesterone (P4)
P4 is measured to determine the following: if the woman has ovulated, when ovulation occurred, if the woman has/had an ectopic pregnancy or if the woman had a miscarriage. Progesterone levels will surge JUST before ovulation and should continue to rise if you become pregnant.
[Return to Index]
Prolactin
The pituitary gland hormone that promotes the woman's milk production after giving birth.
[Return to Index]
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
A hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have irregular menstrual periods, symptoms of excess male hormones, (such as acne, excess hair growth, hair loss associated with a male pattern of balding, weight gain), and development of numerous small cysts on their ovaries. Often they don't ovulate, or ovulate infrequently, causing decreased fertility.
[Return to Index]
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD)
A state-of-the-art procedure used in conjunction with IVF to select embryos for transfer to the uterus that are free of chromosomal abnormalities and specific genetic disorders.
[Return to Index]
Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS)
Screens embryos for missing or additional chromosomes (aneuploidy), which is a leading cause of implantation failure or miscarriage. PGS aims to identify abnormal embryos so they will not be implanted, leaving chromosomally normal embryos to be transferred in an attempt to achieve a successful pregnancy.
[Return to Index]
Preconception genetic screening
Tests prospective parents for over 100 different diseases and syndromes. Genetic screening tests for traits that are common in certain ethnic groups, traits that are recessive and traits that may have some likelihood of causing serious diseases in affected offspring.
[Return to Index]
R
Reproductive endocrinologist (RE)
An obstetrician/gynecologist (ob/gyn) who has taken additional years of training to specialize in reproductive endocrine disorders and infertility.
[Return to Index]
Retrograde ejaculation
A male condition in which semen enters the bladder during ejaculation instead of leaving the penis.
[Return to Index]
Round spermatid nucleus injection (RSNI)
An experimental fertilization technique in which immature sperm cells are removed from the testicles and the genetic material is injected into an egg.
[Return to Index]
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL)
Two or more consecutive miscarriages (spontaneous pregnancy losses) that occur before the gestations reach 20 weeks. Recurrent miscarriages can be attributed to a variety of factors, including genetic defects, an abnormally shaped uterus, fibroids, scar tissue, hormonal imbalances or other conditions.
[Return to Index]
S
Semen analysis (SA)
An examination that assesses a man's sperm count, morphology and motility.
[Return to Index]
Sonohysterogram (SHG)
This is an ultrasound examination that provides information about the uterus and the fallopian tubes, without using x-rays or an anesthetic. It is done shortly after the end of your period and usually before ovulation. Fluid is inserted into the uterus and ultrasound pictures are taken; then a "dye" is infused in order to outline the fallopian tubes.
[Return to Index]
Sperm DNA Fragmentation
DNA fragmentation refers to the situation in which DNA within the sperm contains breaks. Good quality sperm DNA is crucial for successful fertilization of your partner's egg and the normal development of your embryo. Damage to your sperm DNA can occur during sperm production or while it is being stored in your body. A high level of sperm DNA fragmentation reduces the likelihood of pregnancy and is also linked to recurrent miscarriage.
[Return to Index]
Sperm washing
The official term for separating individual sperm from semen. This is done with IUI prior to injecting the sperm into the uterus; and for IVF, this is usually performed after the woman has had her eggs collected, in order to use the sperm for fertilization.
[Return to Index]
T
Testicular epididymal sperm aspiration (TESA)
A simple procedure in which sperm is aspirated from the testicles using a needle. A man may undergo this procedure when his sperm does not exit his penis during ejaculation, or if he has had a vasectomy.
[Return to Index]
Testosterone
A male sex hormone produced in the testicles that aids in the production of sperm.
[Return to Index]
Therapeutic Donor Insemination (TDI)
TDI involves placing cryobanked (frozen) sperm from an anonymous or known donor into the uterus, at the time of ovulation.
[Return to Index]
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
An important hormone in the human reproductive cycle and therefore of particular interest to ART treatments.
[Return to Index]
Therapeutic Donor Insemination (TDI)
TDI involves placing cryobanked (frozen) sperm from an anonymous or known donor into the uterus, at the time of ovulation.
[Return to Index]
Tubal factor infertility
Tubal factor infertility is either a complete or partial blockage and/or scarring of the fallopian tubes, which causes infertility (since either sperm are blocked from meeting the egg or the egg is unable to move to the uterus).
[Return to Index]
U
Unexplained infertility
A diagnostic category used when a man, woman or couple is experiencing infertility, but no cause of it is found.
[Return to Index]
Uterus/Womb
The main female reproductive organ. The fetus develops in the womb during gestation.
[Return to Index]
Ultrasound (US)
The US test assesses ovarian reserve and detects abnormalities of the ovaries, uterus and other structures in the pelvis.
[Return to Index]
V
Vitrification
Vitrification is a technology that is used in the embryo and egg freezing process so that they can be stored for later use. When cells are frozen in a lab, the main focus of the process is to avoid ice crystal formation as the fluid in the cell cools to very low temperatures. Ice crystal formation poses 2 significant and deadly problems for cells. First, an ice crystal is very sharp and will easily shred the cell membrane, killing the cell. Second, as water in the cell turns to ice, it expands in volume, rupturing or killing the cell. Therefore vitrification is one of the processes that was developed to allow cells to be frozen while avoiding the formation of ice.
[Return to Index]
Z
Zygote
The fertilized egg while it is in the fallopian tube in a natural cycle, or immediately after the sperm fertilizes the egg during an IVF cycle.